Turbocharger Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guide for Modern Vehicles

Sharing this:
When your vehicle's performance starts to lag, the culprit might be hiding under the hood in the form of a struggling turbocharger. These powerful components, which can increase engine efficiency by up to 30%, require specific maintenance to function properly throughout their lifespan.
Whether you're noticing decreased acceleration, unusual whistling sounds, or excessive exhaust smoke, understanding how to maintain and troubleshoot your turbocharger can save you thousands in repair costs. At Blue Ridge Auto, we've seen firsthand how proper turbocharger maintenance can extend engine life and maintain vehicle performance.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything from basic maintenance schedules to advanced troubleshooting techniques, helping you keep your turbocharged vehicle running at peak performance for years to come.
How Turbochargers Boost Engine Power and Fuel Efficiency
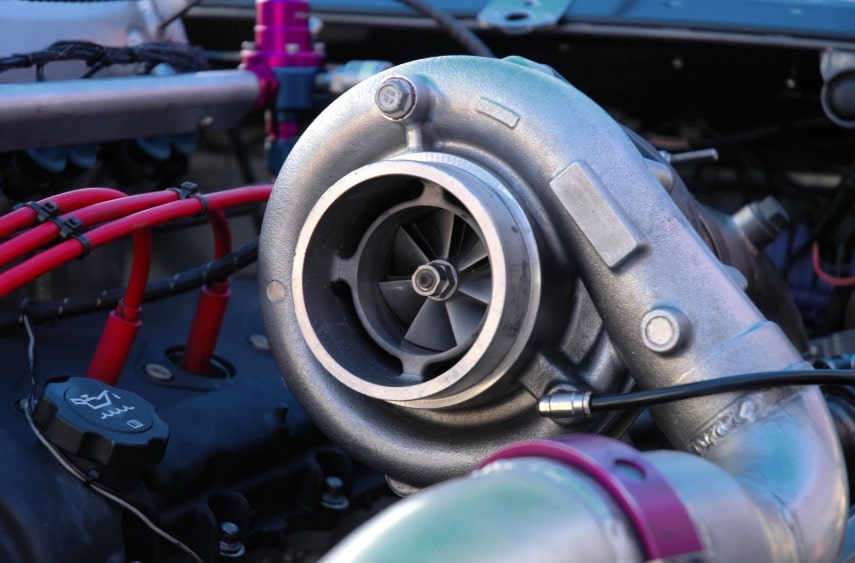

A turbocharger is essentially an air compressor that increases the power output of an engine by forcing extra air into the combustion chamber. This seemingly simple device consists of several critical components working in harmony: the turbine wheel, compressor wheel, center housing, bearings, and wastegate.
The turbine wheel captures energy from the exhaust gases, which then spins the compressor wheel through a connecting shaft. This process forces more air into the engine's cylinders, allowing more fuel to be burned and creating more power from each explosion in the combustion chamber. Modern vehicles often use variable geometry turbochargers that can adjust their output based on driving conditions.
According to industry statistics from 2024, over 60% of new vehicles now come equipped with turbochargers, up from just 35% in 2018. This significant increase demonstrates manufacturers' commitment to balancing performance with fuel efficiency requirements.
Understanding how your specific turbocharger operates is crucial for proper maintenance. Most passenger vehicles use single turbochargers, while performance and diesel vehicles might utilize twin or sequential turbocharger setups for optimized power delivery across different RPM ranges.
Maintenance Habits That Prevent Turbocharger Failure
Regular maintenance is your first line of defense against turbocharger failure. Following these proven practices can significantly extend your turbocharger's operational life:
Oil Quality and Change Intervals
Your turbocharger's bearings spin at incredible speeds, often exceeding 150,000 RPM. This creates extreme heat and stress that only proper lubrication can manage. Always:
- Use manufacturer-recommended synthetic oils designed for turbocharged engines
- Follow strict oil change intervals (typically every 5,000 miles or less for turbocharged vehicles)
- Check oil levels weekly, as turbochargers consume oil faster than naturally aspirated engines
Oil contamination is particularly damaging to turbochargers. Even small metal particles can score bearing surfaces, creating a cascade of damage. At Blue Ridge Auto, we recommend using high-quality oil filters specifically designed for turbocharged applications and never extending oil change intervals beyond manufacturer specifications.
Proper Warm-up and Cool-down Procedures
One of the most common causes of premature turbocharger failure is improper operating procedures. Before driving aggressively, allow your engine to reach normal operating temperature, typically 2-3 minutes of idle time. This ensures oil properly circulates through the turbocharger bearings.
Equally important is the cool-down period. After highway driving or any situation where the turbocharger has been working hard, allow the engine to idle for 30-60 seconds before shutting it off. This prevents oil from "coking" (burning) inside the turbocharger when heat builds up without circulation.
These simple habits can add years to your turbocharger's operational life and prevent the formation of carbon deposits that restrict turbocharger movement.
Identify and Fix the Most Frequent Turbocharger Issues
Turbochargers typically show specific symptoms when they begin to fail. Recognizing these early warning signs can prevent catastrophic damage to both the turbocharger and engine. Our diagnostic experts at Blue Ridge Auto have compiled this troubleshooting guide based on thousands of turbocharger inspections.
Lack of Power and Poor Acceleration
When your vehicle feels sluggish despite pressing the accelerator, your turbocharger may not be providing the expected boost. Common causes include:
- Boost leaks from cracked or disconnected hoses
- Clogged air filters that are restricting airflow
- Carbon buildup on the compressor or turbine wheels
- Wastegate issues that are preventing proper boost regulation
The solution typically involves a thorough inspection of the entire intake and exhaust system. Pressure testing can identify leaks that might be invisible to the naked eye. In many cases, simply replacing worn hoses and clamps can restore proper boost pressure and performance.
Modern vehicles store boost-related fault codes that can be retrieved through diagnostic scanning. Advanced diagnostic tools like those used in our evolution of car diagnostic services can pinpoint specific components that require attention.
Unusual Noises: Whistling, Whining, or Rattling
Turbochargers produce a distinctive sound during normal operation, but certain noises indicate developing problems:
A high-pitched whistle often indicates an exhaust leak before the turbocharger or a crack in the turbocharger housing. Grinding or rattling suggests internal damage to the turbine or compressor wheels, potentially from foreign object damage or bearing failure.
The most concerning sound is a loud whining that increases with engine RPM, which typically indicates bearing wear. This requires immediate attention as complete bearing failure can send metal fragments into your engine, causing extensive damage.
Diagnosing turbocharger noises requires specialized equipment and experience. A mechanic with turbocharger expertise can use a mechanic's stethoscope and other diagnostic tools to isolate the exact source of unusual sounds.
Excessive Smoke from the Exhaust
Our technicians have developed specialized smoke analysis protocols that help identify the exact cause of exhaust issues in turbocharged vehicles. The following color and timing of exhaust smoke provide valuable diagnostic information:
- Blue Smoke: Typically indicates oil consumption issues, often caused by worn turbocharger seals allowing oil to enter the combustion chamber. This commonly occurs during acceleration when boost pressure overcomes the resistance of weakened seals.
- Black Smoke: Suggests incomplete fuel combustion, potentially from a turbocharger delivering inconsistent air pressure or a wastegate that's failing to regulate boost properly.
- White Smoke: If they persist after warm-up, they might indicate coolant entering the combustion chamber through cracked turbocharger components, a serious condition requiring immediate repair.
High-Tech Diagnostic Methods for Accurate Turbocharger Troubleshooting
When basic troubleshooting doesn't resolve performance issues, modern diagnostic techniques can provide deeper insights. The evolution of car diagnostic services has made turbocharger assessment significantly more precise.
Boost Pressure Testing
Measuring actual boost pressure against manufacturer specifications is fundamental to turbocharger diagnosis. This test involves connecting a pressure gauge to the intake system while monitoring engine performance under load conditions.
In 2025, most professional shops use digital pressure transducers that can record boost patterns throughout the RPM range, creating visual representations of turbocharger performance. Normal boost patterns show smooth pressure increases that plateau at the manufacturer's specified limit.
Erratic readings often point to wastegate issues, while consistently low readings suggest internal turbocharger problems or system leaks. Modern vehicles typically target between 8-15 PSI of boost for standard applications, while performance models might generate 20+ PSI.
Shaft Play Measurement
Excessive shaft movement in any direction indicates bearing wear. Professional mechanics use dial indicators to measure shaft movement with the turbocharger removed from the vehicle.
Manufacturer specifications typically allow for 0.002-0.004 inches of movement. Anything more suggests bearing deterioration. This precise measurement requires specialized tools and training but provides definitive evidence of internal turbocharger condition before disassembly.
Know When to Rebuild or Replace a Failing Turbocharger
The eternal question facing owners of turbocharged vehicles is whether to rebuild or replace a failing unit. Several factors influence this decision:
Vehicle Age and Value
For vehicles under 5 years old with less than 60,000 miles, replacement with a new OEM turbocharger typically makes the most sense. The reliability and warranty protection justify the higher cost, especially for vehicles you plan to keep long-term.
For older vehicles or those with higher mileage, remanufactured turbochargers offer an excellent balance of quality and value. These units have been completely disassembled, inspected, and rebuilt with new components to meet strict specifications.
Extent of Damage
Minor issues like worn wastegates, stuck variable vanes, or external leaks can often be repaired without complete turbocharger replacement. However, significant bearing wear, shaft damage, or wheel damage typically necessitates replacement of the entire unit.
Modern turbochargers integrate closely with engine management systems, making proper calibration essential. When replacing turbochargers on vehicles built after 2020, ECU adaptation procedures must be performed to ensure optimal performance and prevent error codes.
A Practical Maintenance Timeline to Extend Turbocharger Life
Creating a maintenance schedule specific to turbocharged vehicles can prevent the most common failures. Based on data from our service department at Blue Ridge Auto, we recommend:
Every 5,000 Miles or 6 Months:
- Change oil and filter using turbo-specific synthetic oil
- Inspect the intercooler and associated hoses for leaks
- Check the air filter condition and replace if dirty
- Examine the turbo oil feed and return lines for leaks or restrictions
Every 15,000 Miles or 18 Months:
- Replace the air filter regardless of apparent condition
- Perform boost pressure testing to verify proper operation
- Clean the mass airflow sensor and throttle body
- Inspect the wastegate actuator operation
Every 30,000 Miles or 36 Months:
- Replace all turbocharger-related hoses and gaskets preventatively
- Perform compression testing to ensure engine health
- Clean or replace the intercooler if performance has degraded
- Check for exhaust leaks that could affect turbocharger performance
Following this schedule can extend turbocharger life by 40-60% compared to vehicles maintained on standard intervals, according to our workshop data compiled from 2020-2025.
Real-World Results: How Preventative Care Saved a Turbocharged SUV
In 2024, a customer brought their 2019 turbocharged SUV to our shop with 78,000 miles, reporting occasional power loss and a check engine light. Initial diagnostics revealed borderline low boost pressure and early signs of oil contamination affecting turbocharger performance.
Rather than waiting for complete failure, we recommended our preventative maintenance package, which included:
- Complete oil system flush with specialized cleaners
- Replacement of oil feed and return lines that showed signs of restriction
- Turbocharger inspection and cleaning without removal
- Installation of an upgraded oil filter with better filtration capabilities
The total investment was approximately $650, compared to the $2,800 that a complete turbocharger replacement would have cost. One year and 15,000 miles later, the vehicle continues to perform flawlessly with proper boost pressure and no warning lights.
This case demonstrates how early intervention based on subtle symptoms can prevent major repairs and extend component life significantly.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should a turbocharger last in a modern vehicle?
With proper maintenance, a modern turbocharger should last between 100,000 to 150,000 miles. However, this varies significantly based on driving habits, maintenance practices, and vehicle design. Vehicles primarily driven on highways typically see longer turbocharger life than those used for frequent short trips or stop-and-go driving.
Premature failures most commonly stem from oil-related issues rather than mechanical defects in the turbocharger itself. Regular oil changes with the correct specification of synthetic oil can often double the service life of these sophisticated components.
What's the average cost to replace a turbocharger?
Turbocharger replacement costs vary widely based on vehicle make and model. For mainstream vehicles, expect to pay between $1,500 and $3,500 for a complete replacement, including parts and labor. Luxury and performance vehicles can cost substantially more, often ranging from $3,000 to $6,000 due to more complex systems and more expensive components.
Remanufactured units typically reduce costs by 30-40% while still providing excellent reliability. Labor represents approximately 40-50% of the total cost due to the complex removal and installation process that often requires removing multiple components for access.
Can I drive with a failing turbocharger?
While technically possible, driving with a failing turbocharger is strongly discouraged. Early symptoms like reduced power or unusual noises might seem minor, but continued operation can lead to catastrophic failure where turbocharger fragments enter the engine, causing extensive damage.
Additionally, a failing turbocharger often leaks oil, which can be drawn into the intake system and cause hydrolock, a serious condition that can bend engine components. At minimum, operating with a failing turbocharger increases fuel consumption and emissions while decreasing performance.
When symptoms appear, limiting driving to necessary trips at reduced speed until repairs can be completed is the safest approach.
Is it normal for a turbocharged engine to consume more oil?
Some oil consumption is normal in turbocharged engines, typically between a quart every 3,000-5,000 miles. This consumption occurs because turbochargers use engine oil for both lubrication and cooling, operating at extremely high temperatures that can cause some oil vaporization.
However, consumption exceeding a quart every 1,000 miles indicates a potential problem that should be investigated. Modern turbocharged engines (built after 2018) have improved seal designs that significantly reduce oil consumption compared to earlier generations. Regular monitoring of oil levels is essential for turbocharged vehicles, with checks recommended at least every second fuel fill-up.
Can aftermarket performance modifications damage my turbocharger?
Aftermarket modifications that increase boost pressure without supporting upgrades can significantly reduce turbocharger lifespan. Simple "tune" modifications that increase boost by 2-3 PSI typically remain within safety margins, but more aggressive tuning without upgrading cooling systems, fuel delivery, and potentially the turbocharger itself creates substantial risk.
Industry data shows that turbochargers on modified vehicles without supporting upgrades fail at approximately twice the rate of stock configurations. If you're considering performance modifications, a comprehensive approach that addresses all affected systems is essential for reliability.
Some manufacturers now use tamper detection systems that can identify unauthorized modifications and potentially affect warranty coverage.
Extend Turbocharger Life and Avoid Major Repairs with Smart Maintenance
Proper turbocharger maintenance is not just about avoiding expensive repairs, it's about maintaining vehicle performance, efficiency, and reliability. By understanding how your turbocharger functions, recognizing early warning signs of trouble, and following a comprehensive maintenance schedule, you can enjoy the performance benefits of turbocharging without unexpected breakdowns.
Remember that professional diagnostic equipment and experience make a significant difference when addressing turbocharger issues. If you're experiencing any symptoms mentioned in this guide, we encourage you to seek a thorough evaluation before minor issues develop into major repairs. Your turbocharged vehicle represents a significant investment; protecting that investment with proper care simply makes good sense.
Contact Blue Ridge Automotive to Maximize Vehicle Reliability and Efficiency
We specialize in digital solutions tailored to your auto repair business. With decades of experience and a skilled team, Blue Ridge Auto helps clients elevate performance and meet measurable goals through reliable and efficient service delivery.Contact Blue Ridge Auto to schedule a consultation and discover how our team can support your vehicle’s long-term reliability with precision diagnostics and repair solutions.



